Amusement park physics roller coaster
Amusement Park Physics Roller Coaster. As you might guess a roller coaster is not all thrilling adventure. Not only did disneyland usher in a new era for amusement parks it also helped bring about some radical changes in roller coaster design. It s quite different from what we experience on a daily basis. Are you really in danger when you are taking those hairpin turns and death defying loops on a roller coaster.
 Amusement Park Physics Roller Coaster From learner.org
Amusement Park Physics Roller Coaster From learner.org
Amusement park physics interactive. There are notable disadvantages such as the money and time involved in bringing 30 kids to the park as well as logistic problems. There s probably a lot of physics involved too. The two most important forms for amusement park rides are kinetic energy and potential energy. Are you really in danger when you are taking those hairpin turns and death defying loops on a roller coaster. Physics of roller coasters teacher resource guide 2 201 s.
Not only did disneyland usher in a new era for amusement parks it also helped bring about some radical changes in roller coaster design.
As you might guess a roller coaster is not all thrilling adventure. Amusement park physics you ve studied the motion of a snowboarder in the previous section and analyzed how potential and kinetic energy changes throughout that motion. It has a mass of 800 kg 1760 lbs. As you might guess a roller coaster is not all thrilling adventure. What makes amusement park rides so much fun is the forces your body experiences when you re on them. A clothoid is a section of a spiral in which the radius is constantly changing.
 Source: physicsclassroom.com
Source: physicsclassroom.com
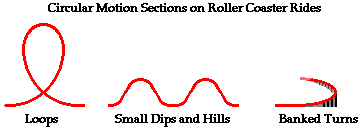
A clothoid is a section of a spiral in which the radius is constantly changing. The history of this ride reflects a constant search for greater and more death defying thrills. The most obvious section on a roller coaster where centripetal acceleration occurs is within the so called clothoid loops. History of amusement park physics an amusement park may not seem at first the ideal place for a study of physics. Amusement park physics you ve studied the motion of a snowboarder in the previous section and analyzed how potential and kinetic energy changes throughout that motion.
 Source: learner.org
Source: learner.org
Up until this time coasters were built out of wood which limited the way loops could be handled. The most obvious section on a roller coaster where centripetal acceleration occurs is within the so called clothoid loops. Imagine a roller coaster ride at an amusement park. Amusement park physics is inspired by programs from the mechanical universe and beyond. What makes amusement park rides so much fun is the forces your body experiences when you re on them.
 Source: prezi.com
Source: prezi.com
Discover how amusement park rides use the laws of physics to simulate danger while keeping the rides safe. The most obvious section on a roller coaster where centripetal acceleration occurs is within the so called clothoid loops. Imagine a roller coaster ride at an amusement park. Amusement park physics you ve studied the motion of a snowboarder in the previous section and analyzed how potential and kinetic energy changes throughout that motion. Roller coaster loops assume a tear dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as a clothoid.
 Source: learner.org
Source: learner.org
There are turns twists and rapid acceleration. History of amusement park physics an amusement park may not seem at first the ideal place for a study of physics. Some people feel it supports a goof off image of physics. Amusement park physics interactive. Imagine a roller coaster ride at an amusement park.
 Source: physicsclassroom.com
Source: physicsclassroom.com
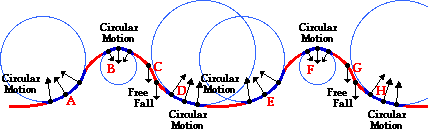
As you might guess a roller coaster is not all thrilling adventure. Understanding amusement park physics is a great way to give you an appreciation of the dynamics of the various rides. Discover how amusement park rides use the laws of physics to simulate danger while keeping the rides safe. In 1959 disney introduced the matterhorn the first tubular steel coaster. In a roller coaster loop riders are pushed inwards toward the center of the loop by forces resulting from the car seat at the loop s bottom and by gravity at the loop s top.
 Source: decorea321.blogspot.com
Source: decorea321.blogspot.com
Amusement park physics interactive. Understanding amusement park physics is a great way to give you an appreciation of the dynamics of the various rides. In a roller coaster loop riders are pushed inwards toward the center of the loop by forces resulting from the car seat at the loop s bottom and by gravity at the loop s top. A clothoid is a section of a spiral in which the radius is constantly changing. What makes amusement park rides so much fun is the forces your body experiences when you re on them.
 Source: new.learningscience.org
Source: new.learningscience.org
As you might guess a roller coaster is not all thrilling adventure. There are notable disadvantages such as the money and time involved in bringing 30 kids to the park as well as logistic problems. For many people there is only one reason to go to an amusement park. In 1959 disney introduced the matterhorn the first tubular steel coaster. The two most important forms for amusement park rides are kinetic energy and potential energy.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The physics of roller coaster loops. It has a mass of 800 kg 1760 lbs. The most obvious section on a roller coaster where centripetal acceleration occurs is within the so called clothoid loops. Imagine a roller coaster ride at an amusement park. Roller coaster loops assume a tear dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as a clothoid.
 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Understanding amusement park physics is a great way to give you an appreciation of the dynamics of the various rides. Amusement park physics is inspired by programs from the mechanical universe and beyond. Roller coaster loops assume a tear dropped shape that is geometrically referred to as a clothoid. We ll assume that your coaster is a single car coaster running on a frictionless track. Some people feel it supports a goof off image of physics.
 Source: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Source: www1.grc.nasa.gov
Some people call it the scream machine with good reason. The most obvious section on a roller coaster where centripetal acceleration occurs is within the so called clothoid loops. For many people there is only one reason to go to an amusement park. The history of this ride reflects a constant search for greater and more death defying thrills. In a roller coaster loop riders are pushed inwards toward the center of the loop by forces resulting from the car seat at the loop s bottom and by gravity at the loop s top.
 Source: wsparrow.blogspot.com
Source: wsparrow.blogspot.com
Some people call it the scream machine with good reason. What makes amusement park rides so much fun is the forces your body experiences when you re on them. Some people feel it supports a goof off image of physics. The acceleration due to gravity is 32 ft s s. There s probably a lot of physics involved too.
 Source: freetech4teachers.com
Source: freetech4teachers.com
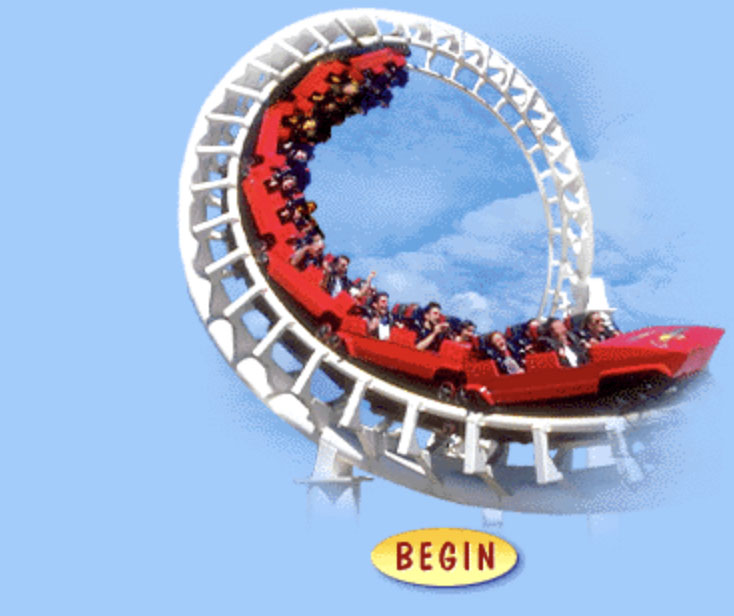
It s quite different from what we experience on a daily basis. The physics of roller coaster loops. Start building your coaster by clicking on the begin button. Understanding amusement park physics is a great way to give you an appreciation of the dynamics of the various rides. Energy energy comes in many forms.
 Source: shop.sciencefirst.com
Source: shop.sciencefirst.com
In a roller coaster loop riders are pushed inwards toward the center of the loop by forces resulting from the car seat at the loop s bottom and by gravity at the loop s top. Imagine a roller coaster ride at an amusement park. Are you really in danger when you are taking those hairpin turns and death defying loops on a roller coaster. The physics of roller coaster loops. The history of this ride reflects a constant search for greater and more death defying thrills.
 Source: induced.info
Source: induced.info
For many people there is only one reason to go to an amusement park. Understanding amusement park physics is a great way to give you an appreciation of the dynamics of the various rides. Are you really in danger when you are taking those hairpin turns and death defying loops on a roller coaster. Amusement park physics you ve studied the motion of a snowboarder in the previous section and analyzed how potential and kinetic energy changes throughout that motion. Not only did disneyland usher in a new era for amusement parks it also helped bring about some radical changes in roller coaster design.
 Source: learner.org
Source: learner.org
Up until this time coasters were built out of wood which limited the way loops could be handled. Some people feel it supports a goof off image of physics. A clothoid is a section of a spiral in which the radius is constantly changing. History of amusement park physics an amusement park may not seem at first the ideal place for a study of physics. There s probably a lot of physics involved too.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title amusement park physics roller coaster by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







