Bonding in molecules
Bonding In Molecules. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. Chemical bonds are the linkages or associations between two or more atoms that together form molecules of compounds. For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration. Chemical bonding any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules ions crystals and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world.
 Chemical Bonds Anatomy And Physiology I From courses.lumenlearning.com
Chemical Bonds Anatomy And Physiology I From courses.lumenlearning.com
The two main types of bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. In molecules consisting of metals the bond type is called metallic. Examples of chemical bonds. The bond dipoles are colored magenta and the resulting molecular dipole is colored blue. A hydrogen bond is effectively a strong example of an interaction between two permanent dipoles. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less equally between each other.
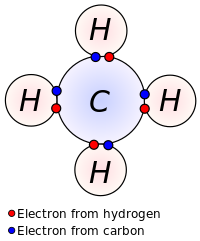
But they are shared with all of the atoms together not between individuals.
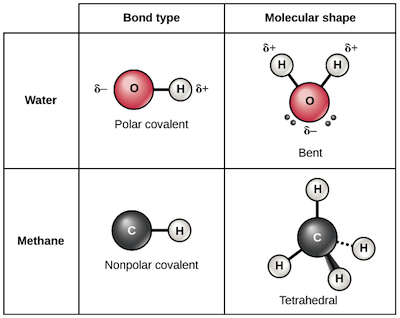
Chemical bonds are the linkages or associations between two or more atoms that together form molecules of compounds. Chemical bonds are the linkages or associations between two or more atoms that together form molecules of compounds. The name scientists use to explain the electron relationship in these molecules is called the electron sea theory. The bond dipoles are colored magenta and the resulting molecular dipole is colored blue. A hydrogen bond is effectively a strong example of an interaction between two permanent dipoles. For example in a water molecule two bonds connect the two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom resulting in the formation of a water molecule.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. The name scientists use to explain the electron relationship in these molecules is called the electron sea theory. A hydrogen bond is effectively a strong example of an interaction between two permanent dipoles. There are two secondary types of covalent bonds that are relevant to biology polar bonds and hydrogen bonds.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Examples of chemical bonds. But they are shared with all of the atoms together not between individuals. In an ionic bond an electron from one atom spends more time associated with the nucleus and electron orbitals of the other atom essentially donated. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero. Chemical bonding any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules ions crystals and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world.
 Source: www2.chemistry.msu.edu
Source: www2.chemistry.msu.edu
A hydrogen bond is effectively a strong example of an interaction between two permanent dipoles. The bonding electrons in a molecule or ion will on average be closer to the more electronegative atom more frequently than the less electronegative one giving rise to partial charges on each atom and causing electrostatic forces between molecules or ions. For example in a water molecule two bonds connect the two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom resulting in the formation of a water molecule. For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration. Our basis for understanding chemical bonding and the structures of molecules is the electron orbital description of the structure and valence of atoms as provided by quantum mechanics.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Examples of chemical bonds. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less equally between each other. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero. For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. Like in molecules with covalent bonds the electrons are shared. Examples of chemical bonds. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. The two main types of bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The bond dipoles are colored magenta and the resulting molecular dipole is colored blue. For example in a water molecule two bonds connect the two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom resulting in the formation of a water molecule. Examples of chemical bonds. There are two secondary types of covalent bonds that are relevant to biology polar bonds and hydrogen bonds. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The two main types of bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Examples of chemical bonds. Chemical bonds are the linkages or associations between two or more atoms that together form molecules of compounds. In an ionic bond an electron from one atom spends more time associated with the nucleus and electron orbitals of the other atom essentially donated. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
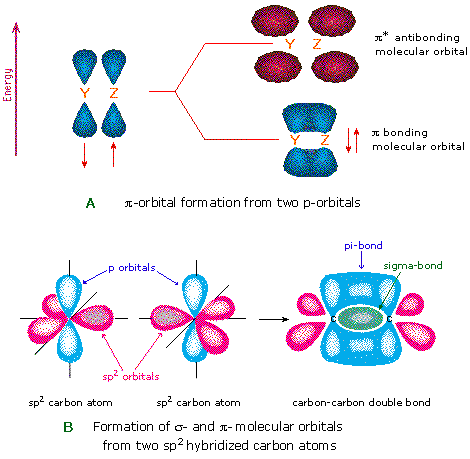
The pair of shared electrons forms a new orbit that extends around the nuclei of both atoms producing a molecule. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. Our basis for understanding chemical bonding and the structures of molecules is the electron orbital description of the structure and valence of atoms as provided by quantum mechanics. For example in a water molecule two bonds connect the two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom resulting in the formation of a water molecule. The name scientists use to explain the electron relationship in these molecules is called the electron sea theory.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
In molecules consisting of metals the bond type is called metallic. For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration. The pair of shared electrons forms a new orbit that extends around the nuclei of both atoms producing a molecule. The bonding electrons in a molecule or ion will on average be closer to the more electronegative atom more frequently than the less electronegative one giving rise to partial charges on each atom and causing electrostatic forces between molecules or ions. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less equally between each other.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The two main types of bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. For example in a water molecule two bonds connect the two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom resulting in the formation of a water molecule. The pair of shared electrons forms a new orbit that extends around the nuclei of both atoms producing a molecule. But they are shared with all of the atoms together not between individuals. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Chemical bonds are the linkages or associations between two or more atoms that together form molecules of compounds. We assume an understanding of the periodicity of the elements based on the nuclear structure of the atom and our deductions concerning valence based on electron orbitals. In molecules consisting of metals the bond type is called metallic. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero. Examples of chemical bonds.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The bonding electrons in a molecule or ion will on average be closer to the more electronegative atom more frequently than the less electronegative one giving rise to partial charges on each atom and causing electrostatic forces between molecules or ions. Our basis for understanding chemical bonding and the structures of molecules is the electron orbital description of the structure and valence of atoms as provided by quantum mechanics. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero. In an ionic bond an electron from one atom spends more time associated with the nucleus and electron orbitals of the other atom essentially donated. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less equally between each other.
 Source: sciencing.com
Source: sciencing.com
Examples of chemical bonds. Chemical bonding any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules ions crystals and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world. Our basis for understanding chemical bonding and the structures of molecules is the electron orbital description of the structure and valence of atoms as provided by quantum mechanics. In the linear configuration bond angle 180º the bond dipoles cancel and the molecular dipole is zero. In molecules consisting of metals the bond type is called metallic.
 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
For other bond angles 120 to 90º the molecular dipole would vary in size being largest for the 90º configuration. Chemical bonding any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules ions crystals and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world. For example in a water molecule two bonds connect the two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom resulting in the formation of a water molecule. In an ionic bond an electron from one atom spends more time associated with the nucleus and electron orbitals of the other atom essentially donated. In molecules consisting of metals the bond type is called metallic.
 Source: www2.chemistry.msu.edu
Source: www2.chemistry.msu.edu
But they are shared with all of the atoms together not between individuals. Like in molecules with covalent bonds the electrons are shared. The pair of shared electrons forms a new orbit that extends around the nuclei of both atoms producing a molecule. In an ionic bond an electron from one atom spends more time associated with the nucleus and electron orbitals of the other atom essentially donated. Covalent bonding is where atoms share electrons more or less equally between each other.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title bonding in molecules by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





