Pith of a tree
Pith Of A Tree. It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. Tree pith is generally present in young growth. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. The cells are large but have thin walls.
 Inside Woody Twigs From backyardnature.net
Inside Woody Twigs From backyardnature.net
The cells are large but have thin walls. In the trunk and older branches it is often mostly replaced by a woody substance called xylem. It is soft and spongy. The xylem in turn is encircled by a ring of phloem. It is made up of distinctive parenchyma cells. The pith functions by transporting nutrients throughout the plant and storing nutrients within its cells.
Pith is the tissue that is located in a plant s stem and roots.
It is soft and spongy. It is soft and spongy. The roots of woody dicots and conifers develop only a cortex the pith is absent the innermost. General features of the tree body and the inner region the pith although among many of the monocotyledons an advanced class of angiosperms including the palms and lilies the ground tissue is amorphous and no regions can be discerned. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem.
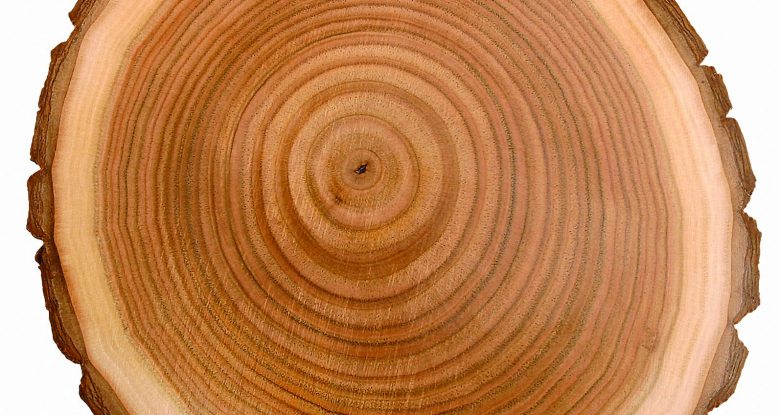 Source: woodcarvingillustrated.com
Source: woodcarvingillustrated.com
It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. The pith functions by transporting nutrients throughout the plant and storing nutrients within its cells. The cells are large but have thin walls. It is soft and spongy. Tree pith is generally present in young growth.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. It is soft and spongy. The pith functions by transporting nutrients throughout the plant and storing nutrients within its cells. It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. The cells are large but have thin walls.
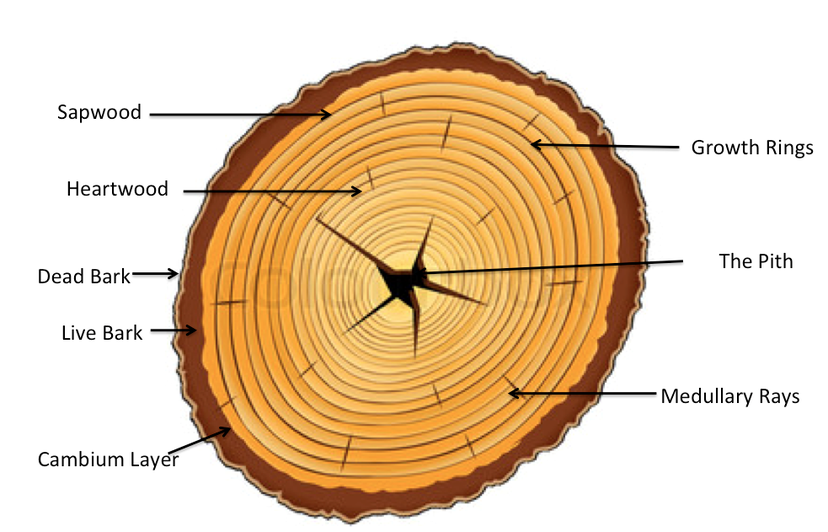 Source: treegrowthstructure.weebly.com
Source: treegrowthstructure.weebly.com
It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. Tree pith is generally present in young growth. The xylem in turn is encircled by a ring of phloem. It is soft and spongy. The cells are large but have thin walls.
 Source: onetreestudio.com.au
Source: onetreestudio.com.au
In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. In eudicotyledons pith is located in the center of the stem in monocotyledons it extends also into flowering stems and roots the pith is encircled by a ring of xylem. Pith or medulla is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants pith is composed of soft spongy parenchyma cells which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. Tree pith is generally present in young growth.
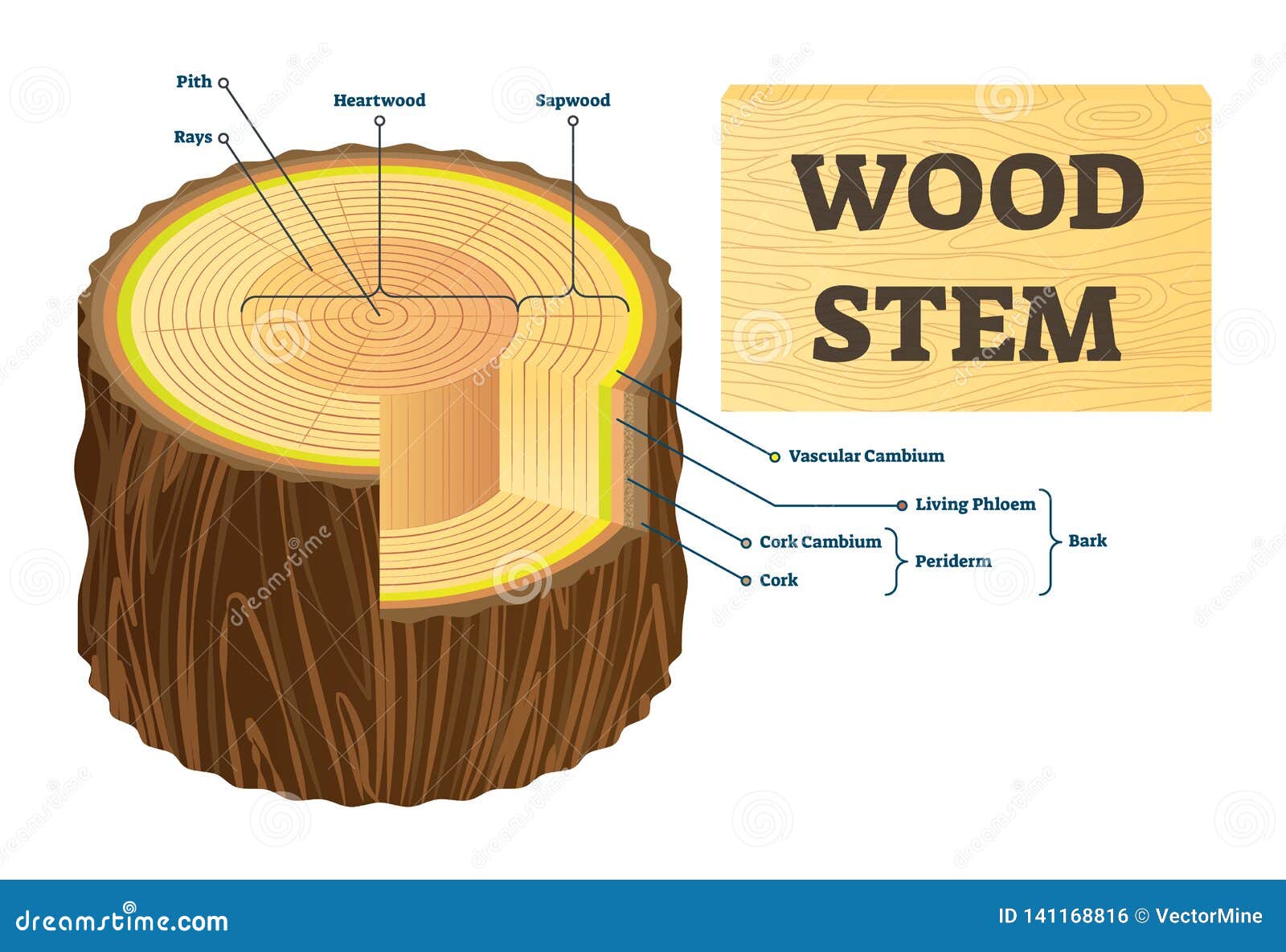 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
Pith or medulla is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants pith is composed of soft spongy parenchyma cells which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. It is soft and spongy. In eudicotyledons pith is located in the center of the stem in monocotyledons it extends also into flowering stems and roots the pith is encircled by a ring of xylem. Tree pith is generally present in young growth.
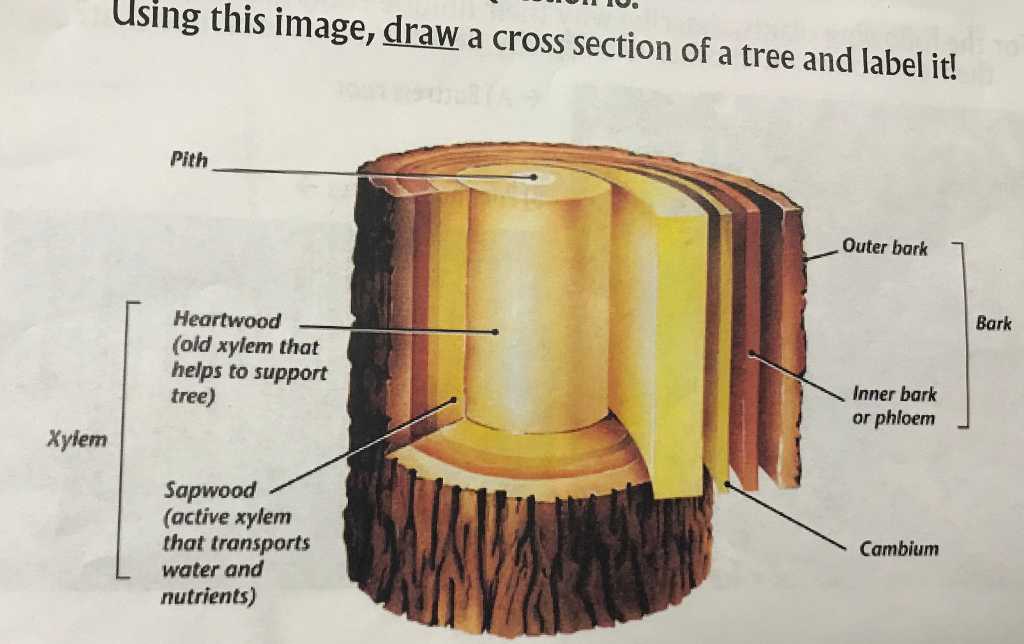 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
It is soft and spongy. Tree pith is generally present in young growth. New pith growth appears white but as it matures it usually turns brown. General features of the tree body and the inner region the pith although among many of the monocotyledons an advanced class of angiosperms including the palms and lilies the ground tissue is amorphous and no regions can be discerned. The cells are large but have thin walls.
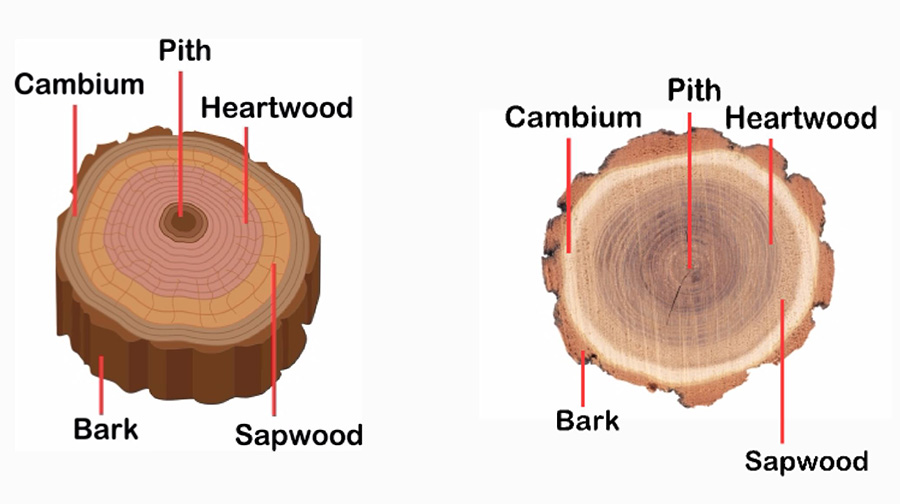 Source: palodurohardwoods.com
Source: palodurohardwoods.com
General features of the tree body and the inner region the pith although among many of the monocotyledons an advanced class of angiosperms including the palms and lilies the ground tissue is amorphous and no regions can be discerned. It is soft and spongy. Tree pith is generally present in young growth. In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem. New pith growth appears white but as it matures it usually turns brown.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
In eudicotyledons pith is located in the center of the stem in monocotyledons it extends also into flowering stems and roots the pith is encircled by a ring of xylem. It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. Pith is the tissue that is located in a plant s stem and roots. The xylem in turn is encircled by a ring of phloem. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits.
 Source: woodcarvingillustrated.com
Source: woodcarvingillustrated.com
In eudicotyledons pith is located in the center of the stem in monocotyledons it extends also into flowering stems and roots the pith is encircled by a ring of xylem. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. It is made up of distinctive parenchyma cells. Tree pith is generally present in young growth. General features of the tree body and the inner region the pith although among many of the monocotyledons an advanced class of angiosperms including the palms and lilies the ground tissue is amorphous and no regions can be discerned.
 Source: www2.palomar.edu
Source: www2.palomar.edu
In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem. It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. It is soft and spongy. Pith is the tissue that is located in a plant s stem and roots. In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem.
 Source: backyardnature.net
Source: backyardnature.net
It is soft and spongy. General features of the tree body and the inner region the pith although among many of the monocotyledons an advanced class of angiosperms including the palms and lilies the ground tissue is amorphous and no regions can be discerned. In the trunk and older branches it is often mostly replaced by a woody substance called xylem. Pith is the tissue that is located in a plant s stem and roots. It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. It can be very bitter on a grapefruit but it s often kind of bland on an orange. In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem. New pith growth appears white but as it matures it usually turns brown. In the trunk and older branches it is often mostly replaced by a woody substance called xylem.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Pith or medulla is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants pith is composed of soft spongy parenchyma cells which store and transport nutrients throughout the plant. Pith is the tissue that is located in a plant s stem and roots. General features of the tree body and the inner region the pith although among many of the monocotyledons an advanced class of angiosperms including the palms and lilies the ground tissue is amorphous and no regions can be discerned. The cells are large but have thin walls. The xylem in turn is encircled by a ring of phloem.
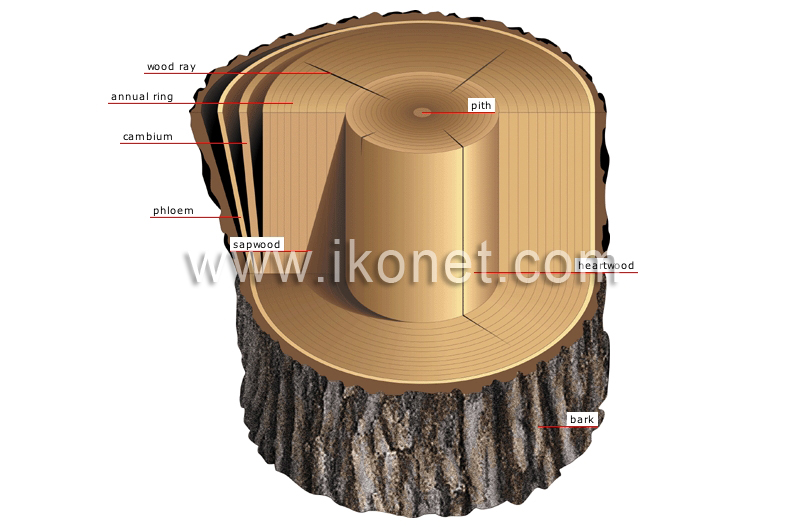 Source: ikonet.com
Source: ikonet.com
The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. Tree pith is generally present in young growth. It is soft and spongy. The xylem in turn is encircled by a ring of phloem. The pith functions by transporting nutrients throughout the plant and storing nutrients within its cells.
 Source: copperman.co.uk
Source: copperman.co.uk
The cells are large but have thin walls. Pith is the tissue that is located in a plant s stem and roots. In some plants the medulla tissue in the middle of the stem may dry out and disintegrate resulting in a hollow stem. The pith is the spongy white substance that s between the peel and the fruit in oranges and other citrus fruits. In eudicotyledons pith is located in the center of the stem in monocotyledons it extends also into flowering stems and roots the pith is encircled by a ring of xylem.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title pith of a tree by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







