Process of fruit ripening
Process Of Fruit Ripening. What happens as the fruit ripens. We d recommend throwing the underripe fruit along. Ripening is associated with change in compositioni e. The timing of tomato fruit ripening is tightly regulated and dependent upon the plant hormone ethylene.
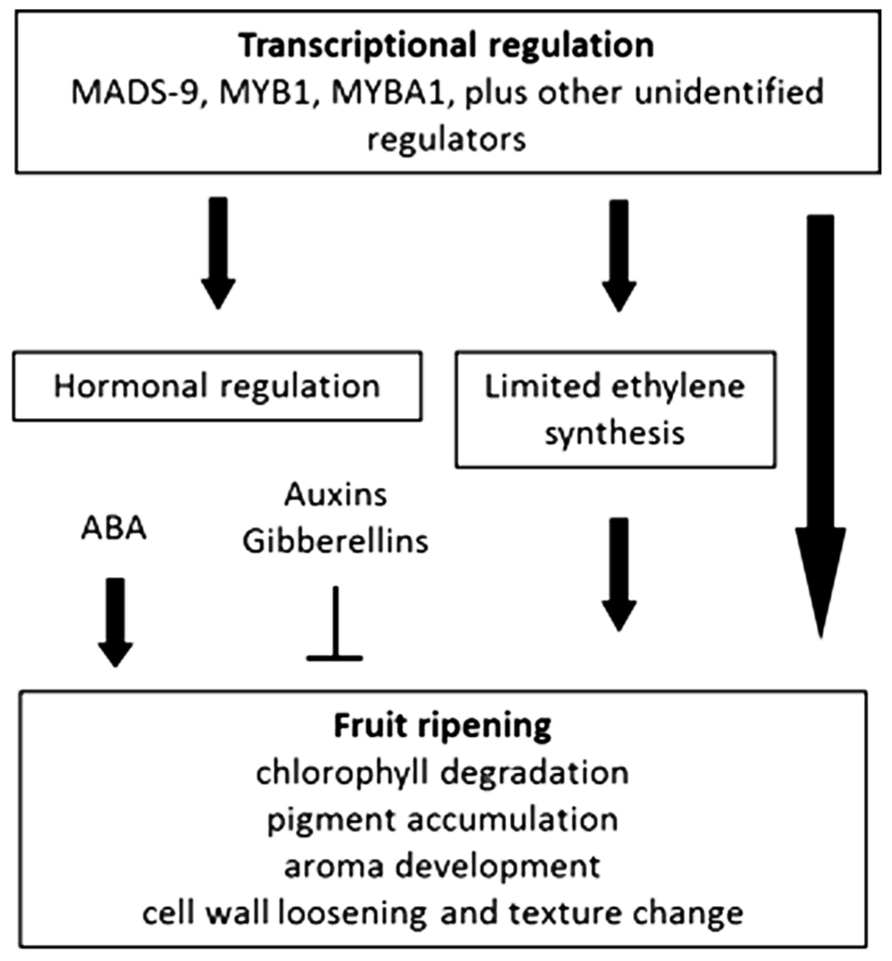 Frontiers Molecular Regulation Of Fruit Ripening Plant Science From frontiersin.org
Frontiers Molecular Regulation Of Fruit Ripening Plant Science From frontiersin.org
One of the important events that the ripening process has is the conversion of starch to sugar. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. What happens as the fruit ripens. This process is particularly obvious in bananas as they ripen. Fruit ripening is a developmental process evolved to foster animal mediated seed dispersal and considerable progress have been made through studies of tomato solanum lycopersicum which is an important vegetable crop as well as the model plant for the solanaceae family. We d recommend throwing the underripe fruit along.
During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose.
Conversion of starch to sugar. Underripe fruits are also fibrous less juicy and have. What happens as the fruit ripens. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. The process of fruit ripening is intimately associated with phenomenon of senescence. This process is particularly obvious in bananas as they ripen.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. Ripening is a process in fruits that causes them to become more palatable in general fruit becomes sweeter less green typically redder and softer as it ripens even though the acidity of fruit increases as it ripens the higher acidity level does not make the fruit seem tarter. What happens as the fruit ripens. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
As the plants absorb moisture minerals from the soil and all the necessary components for it to thrive the fruit continues to grow its storage cells expand engorging it with water sugars starches organic acids vitamins and minerals. One of the important events that the ripening process has is the conversion of starch to sugar. On the basis of ripening behavior fruits are classified as climacteric and non climacteric fruits. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. What happens as the fruit ripens.
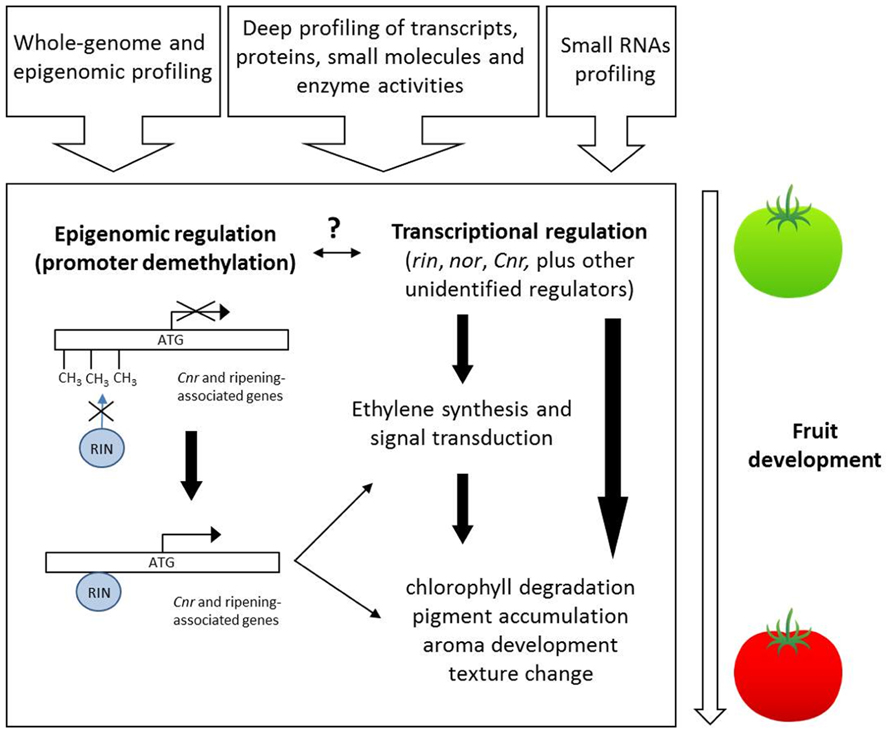 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. Ripening is the process by which fruits attain their desirable flavour quality colour palatable nature and other textural properties. The timing of tomato fruit ripening is tightly regulated and dependent upon the plant hormone ethylene. During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose. Senescence of a plant organ is usually defined as final stage in its growth and development i e ontogeny during which a series of essentially irreversible or deteriorative events occur lead ing to cellular breakdown and death.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
What happens as the fruit ripens. Fruit ripening is a developmental process evolved to foster animal mediated seed dispersal and considerable progress have been made through studies of tomato solanum lycopersicum which is an important vegetable crop as well as the model plant for the solanaceae family. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. Ripening their fruit is a survival tactic used by plants to help them reproduce and multiply. Ripening is a process in fruits that causes them to become more palatable in general fruit becomes sweeter less green typically redder and softer as it ripens even though the acidity of fruit increases as it ripens the higher acidity level does not make the fruit seem tarter.
 Source: chemtronscience.com
Source: chemtronscience.com
The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. Conversion of starch to sugar. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose. Ripening is the process by which fruits attain their desirable flavour quality colour palatable nature and other textural properties.
 Source: evikon.eu
Source: evikon.eu
During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose. Ripening is the process by which fruits attain their desirable flavour quality colour palatable nature and other textural properties. On the basis of ripening behavior fruits are classified as climacteric and non climacteric fruits. Ripening is associated with change in compositioni e. One of the important events that the ripening process has is the conversion of starch to sugar.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The timing of tomato fruit ripening is tightly regulated and dependent upon the plant hormone ethylene. Ripening is associated with change in compositioni e. Fruit ripening is a developmental process evolved to foster animal mediated seed dispersal and considerable progress have been made through studies of tomato solanum lycopersicum which is an important vegetable crop as well as the model plant for the solanaceae family. Conversion of starch to sugar. Senescence of a plant organ is usually defined as final stage in its growth and development i e ontogeny during which a series of essentially irreversible or deteriorative events occur lead ing to cellular breakdown and death.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
As the plants absorb moisture minerals from the soil and all the necessary components for it to thrive the fruit continues to grow its storage cells expand engorging it with water sugars starches organic acids vitamins and minerals. Conversion of starch to sugar. The key to ripening fruit at home is to harness naturally occurring ethylene which is a gas that is given off by fruit to aid in its ripening. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. The timing of tomato fruit ripening is tightly regulated and dependent upon the plant hormone ethylene.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The process of fruit ripening is intimately associated with phenomenon of senescence. Fruit ripening is a developmental process evolved to foster animal mediated seed dispersal and considerable progress have been made through studies of tomato solanum lycopersicum which is an important vegetable crop as well as the model plant for the solanaceae family. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. We d recommend throwing the underripe fruit along. During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose.
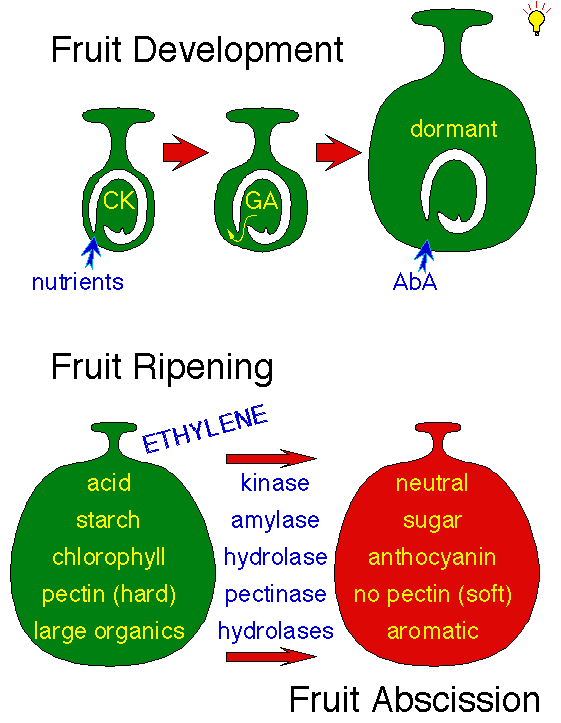 Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
Source: www1.biologie.uni-hamburg.de
One of the important events that the ripening process has is the conversion of starch to sugar. As the plants absorb moisture minerals from the soil and all the necessary components for it to thrive the fruit continues to grow its storage cells expand engorging it with water sugars starches organic acids vitamins and minerals. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. The timing of tomato fruit ripening is tightly regulated and dependent upon the plant hormone ethylene. Senescence of a plant organ is usually defined as final stage in its growth and development i e ontogeny during which a series of essentially irreversible or deteriorative events occur lead ing to cellular breakdown and death.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Senescence of a plant organ is usually defined as final stage in its growth and development i e ontogeny during which a series of essentially irreversible or deteriorative events occur lead ing to cellular breakdown and death. Ripening is associated with change in compositioni e. Ripening their fruit is a survival tactic used by plants to help them reproduce and multiply. What happens as the fruit ripens. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition.
Source: eagri.org
On the basis of ripening behavior fruits are classified as climacteric and non climacteric fruits. Conversion of starch to sugar. On the basis of ripening behavior fruits are classified as climacteric and non climacteric fruits. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. As the plants absorb moisture minerals from the soil and all the necessary components for it to thrive the fruit continues to grow its storage cells expand engorging it with water sugars starches organic acids vitamins and minerals.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Underripe fruits are also fibrous less juicy and have. Underripe fruits are also fibrous less juicy and have. During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose. The process of fruit ripening is intimately associated with phenomenon of senescence. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Ripening is associated with change in compositioni e. During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose. This process is particularly obvious in bananas as they ripen. The fruit ripening process ripening is the process where fruits stages occur in order to reach their natural composition cycle such as texture color flavor and decomposition. Ripening is the process by which fruits attain their desirable flavour quality colour palatable nature and other textural properties.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. Senescence of a plant organ is usually defined as final stage in its growth and development i e ontogeny during which a series of essentially irreversible or deteriorative events occur lead ing to cellular breakdown and death. Ripening is a process in fruits that causes them to become more palatable in general fruit becomes sweeter less green typically redder and softer as it ripens even though the acidity of fruit increases as it ripens the higher acidity level does not make the fruit seem tarter. This effect is attributed to the brix acid ratio. During ripening there is an increase in the breakdown of starch inside the fruit and a corresponding increase in the amount of simple sugars which taste sweet such as sucrose glucose and fructose.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title process of fruit ripening by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







