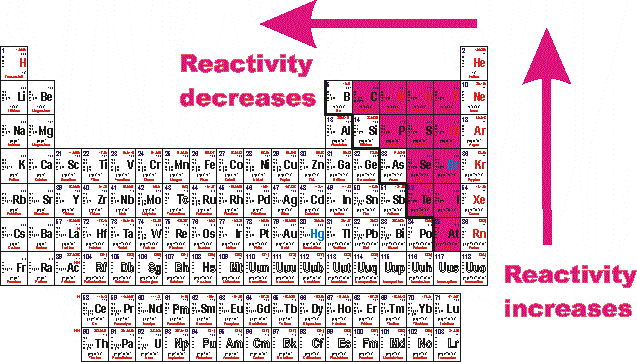
Reactivity of metals periodic table
Reactivity Of Metals Periodic Table. Chemical reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. The metal reactivity sequence also known as the set of operations refers to the organization of metals in the ascending order of their reactivities. That is why as you go up a group chemical reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity.
 What Nonmetals Are Most Chemically Reactive Socratic From socratic.org
What Nonmetals Are Most Chemically Reactive Socratic From socratic.org
They re closely followed by the marginally less reactive group two metals. Some lead to the forming of metal oxides with ambient oxygen. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell. The reactivity of metals varies greatly. Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings. That is why as you go up a group chemical reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity.
And the farther they are from the righ side of the table the weaker their electronegativity is.
The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of. That is why as you go up a group chemical reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. The metals designated as the transition metals in the periodic table are much less reactive and metals such as gold and platinum prop up the bottom of the series exhibiting little in the way of chemical reaction with any everyday reagents. For non metals the farther right up in the table you go the higher the electronegativity. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3.
 Source: crackbmat.com
Source: crackbmat.com
Chemical reactivity decrease as you go down the group. The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of. Chemical reactivity decrease as you go down the group. They re closely followed by the marginally less reactive group two metals. That is why as you go up a group chemical reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity.
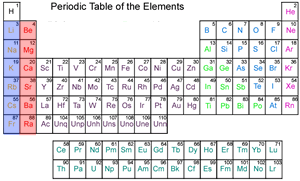 Source: dynamicscience.com.au
Source: dynamicscience.com.au
Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. The reactivity of metals varies greatly. Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. Group 1 metals the most reactive metals in the periodic table head up the rankings.
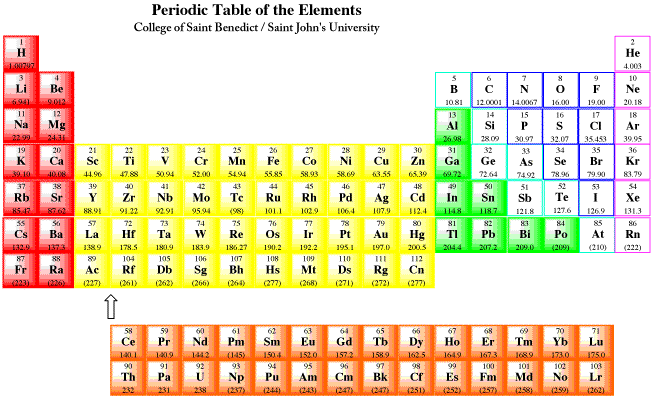 Source: employees.csbsju.edu
Source: employees.csbsju.edu
Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. The metals designated as the transition metals in the periodic table are much less reactive and metals such as gold and platinum prop up the bottom of the series exhibiting little in the way of chemical reaction with any everyday reagents. The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of.
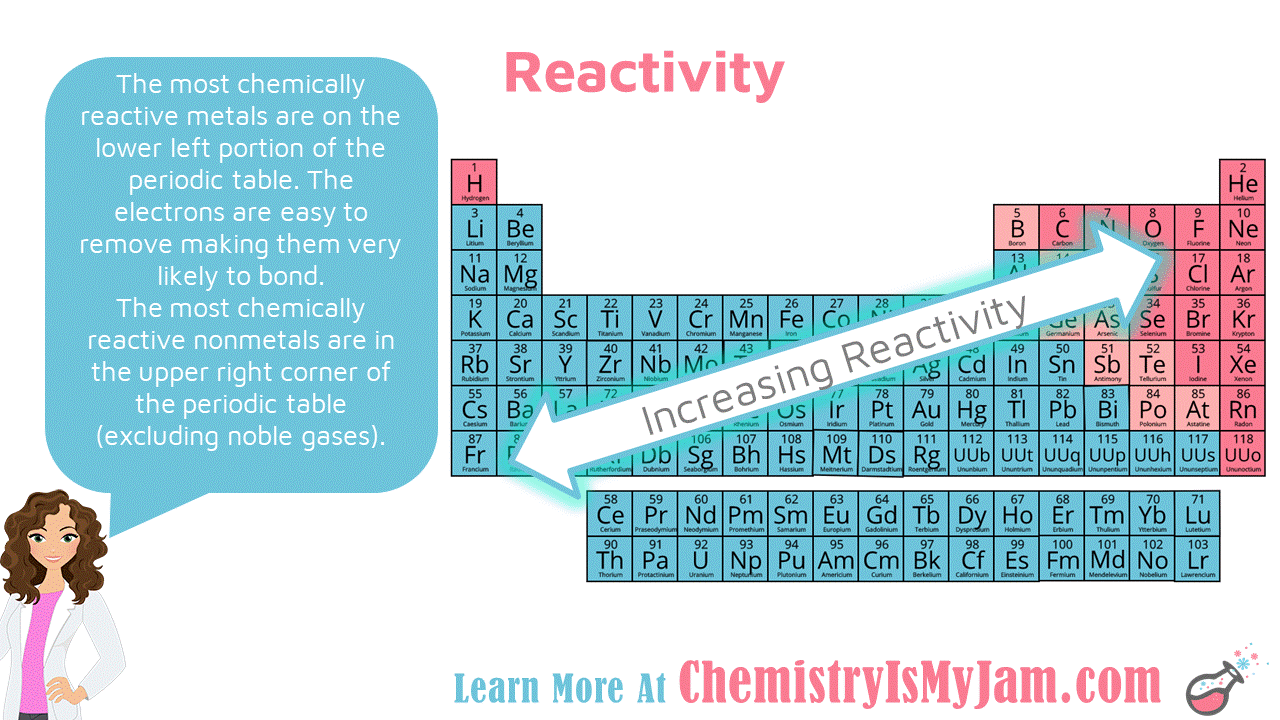 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
For non metals the farther right up in the table you go the higher the electronegativity. That is why as you go up a group chemical reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity. Chemical reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table. The alkali metals are shiny soft highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings.
 Source: chemproject11.weebly.com
Source: chemproject11.weebly.com
The alkali metals are shiny soft highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. And the farther they are from the righ side of the table the weaker their electronegativity is. The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. Group 1 metals the most reactive metals in the periodic table head up the rankings.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
Group 1 metals the most reactive metals in the periodic table head up the rankings. Chemical reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table. That is why as you go up a group chemical reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity. They re closely followed by the marginally less reactive group two metals. Some metals such those in columns 1 and 2 on the periodic table.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Some metals such those in columns 1 and 2 on the periodic table. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. Some metals such those in columns 1 and 2 on the periodic table. Chemical reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The metal reactivity sequence also known as the set of operations refers to the organization of metals in the ascending order of their reactivities. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. For non metals the farther right up in the table you go the higher the electronegativity. Chemical reactivity decrease as you go down the group. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell.
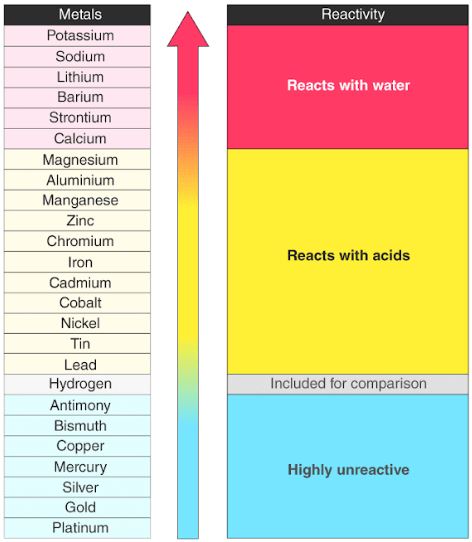 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Chemical reactivity decrease as you go down the group. And the farther they are from the righ side of the table the weaker their electronegativity is. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. The alkali metals are shiny soft highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings.
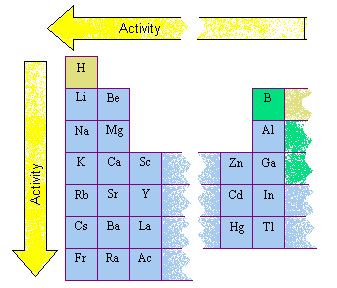 Source: chemed.chem.purdue.edu
Source: chemed.chem.purdue.edu
The outer shell of a metal is therefore less than half full of. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3. The metal reactivity sequence also known as the set of operations refers to the organization of metals in the ascending order of their reactivities. Chemical reactivity decrease as you go down the group.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The alkali metals are shiny soft highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Metals tend to lose electrons and form cations quickly. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell. The reactivity of metals varies greatly. The alkali metals are shiny soft highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Some lead to the forming of metal oxides with ambient oxygen. And the farther they are from the righ side of the table the weaker their electronegativity is. The metals designated as the transition metals in the periodic table are much less reactive and metals such as gold and platinum prop up the bottom of the series exhibiting little in the way of chemical reaction with any everyday reagents. The metal reactivity sequence also known as the set of operations refers to the organization of metals in the ascending order of their reactivities. Chemical reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table.
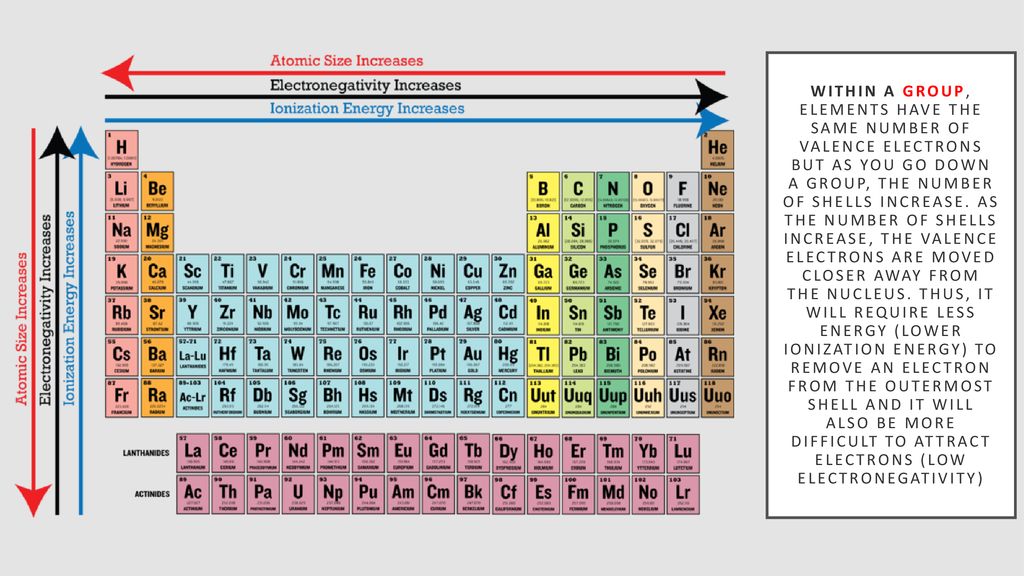 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The reactivity of metals varies greatly. For non metals the farther right up in the table you go the higher the electronegativity. Chemical reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table. Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell.
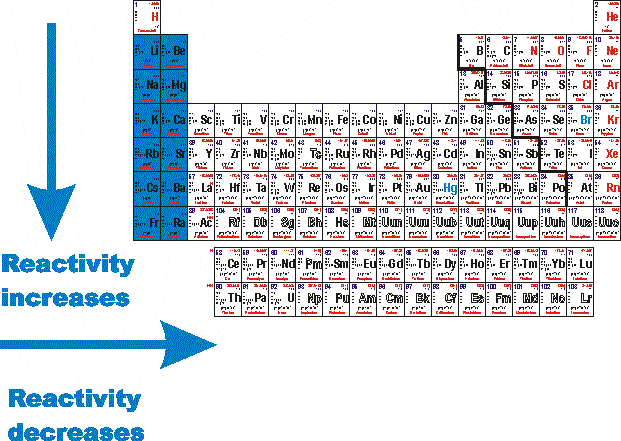 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
They re closely followed by the marginally less reactive group two metals. These metals will have 1 2 or 3 electrons in the outer shell. Some lead to the forming of metal oxides with ambient oxygen. Chemical reactivity decrease as you go down the group. The periodic table shows that metals are found in groups 1 2 and 3.
 Source: compoundchem.com
Source: compoundchem.com
The alkali metals are shiny soft highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. And the farther they are from the righ side of the table the weaker their electronegativity is. Group 1 metals the most reactive metals in the periodic table head up the rankings. For non metals the farther right up in the table you go the higher the electronegativity. Reactivity refers to the tendency of a metal to react with chemicals in its surroundings.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title reactivity of metals periodic table by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.