Sinking of rock layers
Sinking Of Rock Layers. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. Stress at a convergent plate boundary. Stress at a divergent plate boundary. Two dimensional numerical models are used to study the gravity driven sinking of a dense boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt.
 Chapter 4 Rocks And Minerals From volcano.oregonstate.edu
Chapter 4 Rocks And Minerals From volcano.oregonstate.edu
We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. The bending of rock layers due to stress. A monocline is a fold where the rock layers form an s shape as the sides of the rock are compressed. Downward arching rock layer. We analyze models with an infinite array of regularly spaced blocks two and three block clusters and irregularly spaced blocks.
The rising of regions of the earths crust to higher elevations.
It may be caused by natural processes or by human activities. New rock layers are always deposited on top of existing rock layers. I hope that this helps actually its the matching up of rocks of the same age from place to place is called correlation of the. You can remember this type of fold because all the layers of rock are still horizontal going. The upper mantle is also known as the asthenosphere which flows as convection currents. Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall.
 Source: answersingenesis.org
Source: answersingenesis.org
You can remember this type of fold because all the layers of rock are still horizontal going. The bending of rock layers due to stress. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. The definition of subsidence is not restricted by the rate magnitude or area involved in the downward movement. For these reasons it is important to consider the possible effects of sinking in the scour protection design and to understand the mechanisms that could lead to unacceptable sinking of the scour protection the study showed that the sinking is controlled by two mechanisms.
 Source: grade8science.com
Source: grade8science.com
For these reasons it is important to consider the possible effects of sinking in the scour protection design and to understand the mechanisms that could lead to unacceptable sinking of the scour protection the study showed that the sinking is controlled by two mechanisms. We analyze models with an infinite array of regularly spaced blocks two and three block clusters and irregularly spaced blocks. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. Mass shape and spatial arrangement of blocks are the sinking controlling factors. It may be caused by natural processes or by human activities.
 Source: volcano.oregonstate.edu
Source: volcano.oregonstate.edu
Convection occurs in all fluids and is the rising of warm particles and sinking of cool particles. A break in a body of rock along which one block slides relativ. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. For these reasons it is important to consider the possible effects of sinking in the scour protection design and to understand the mechanisms that could lead to unacceptable sinking of the scour protection the study showed that the sinking is controlled by two mechanisms.
Source:
The bending of rock layers due to stress. The definition of subsidence is not restricted by the rate magnitude or area involved in the downward movement. The sinking of the rock layers is called subsidence. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Two dimensional numerical models are used to study the gravity driven sinking of a dense boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. We analyze models with an infinite array of regularly spaced blocks two and three block clusters and irregularly spaced blocks. Mass shape and spatial arrangement of blocks are the sinking controlling factors. Upward arching rock layer. Variation of the block separation can modify the velocity by orders of magnitude.
 Source: answersingenesis.org
Source: answersingenesis.org
Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. We analyze models with an infinite array of regularly spaced blocks two and three block clusters and irregularly spaced blocks. The bending of rock layers due to stress. Upward arching rock layer. Removal of sediment adjacent to the pile destabilizing and infilling of sediment into the scour protection from the surrounding seabed stabilizing.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Convection occurs in all fluids and is the rising of warm particles and sinking of cool particles. So as the material in the upper mantle warms it rises straight up and as it rises it cools and then sinks back down. Mass shape and spatial arrangement of blocks are the sinking controlling factors. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. Irregularly spaced blocks sink much faster than the regularly spaced array.
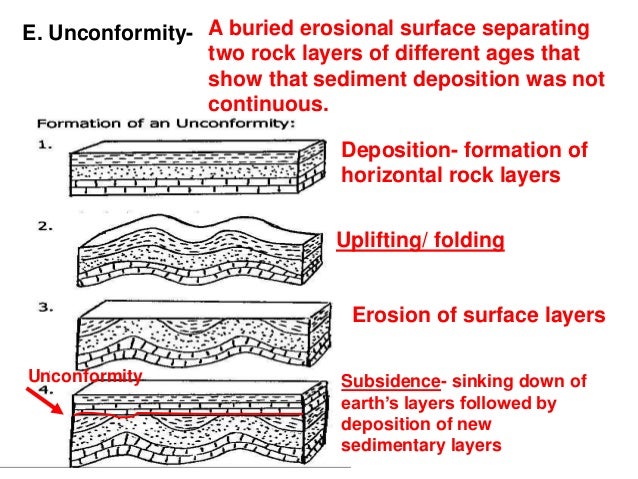 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Two dimensional numerical models are used to study the gravity driven sinking of a dense boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. For these reasons it is important to consider the possible effects of sinking in the scour protection design and to understand the mechanisms that could lead to unacceptable sinking of the scour protection the study showed that the sinking is controlled by two mechanisms. Mass shape and spatial arrangement of blocks are the sinking controlling factors. Removal of sediment adjacent to the pile destabilizing and infilling of sediment into the scour protection from the surrounding seabed stabilizing.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Stress at a divergent plate boundary. New rock layers are always deposited on top of existing rock layers. The sinking of the rock layers is called subsidence. Two dimensional numerical models are used to study the gravity driven sinking of a dense boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. The bending of rock layers due to stress. Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall. A monocline is a fold where the rock layers form an s shape as the sides of the rock are compressed. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion.
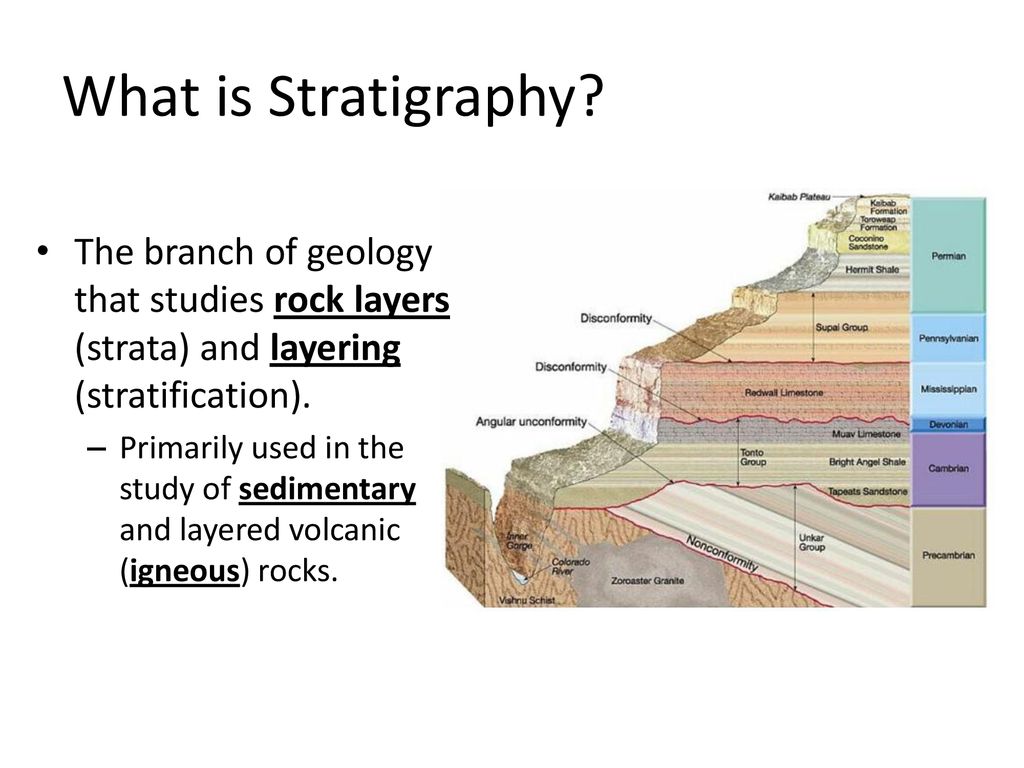 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The sinking of the rock layers is called subsidence. Variation of the block separation can modify the velocity by orders of magnitude. The sinking of the rock layers is called subsidence. Stress at a divergent plate boundary. You can remember this type of fold because all the layers of rock are still horizontal going.
Source:
Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall. Two dimensional numerical models are used to study the gravity driven sinking of a dense boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. The sinking of the rock layers is called subsidence. Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground s surface with little or no horizontal motion. Hanging wall moves down relative to footwall.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
New rock layers are always deposited on top of existing rock layers. Correlating rock layers is comparing two rock layers to each other. Downward arching rock layer. Stress at a divergent plate boundary. Mass shape and spatial arrangement of blocks are the sinking controlling factors.
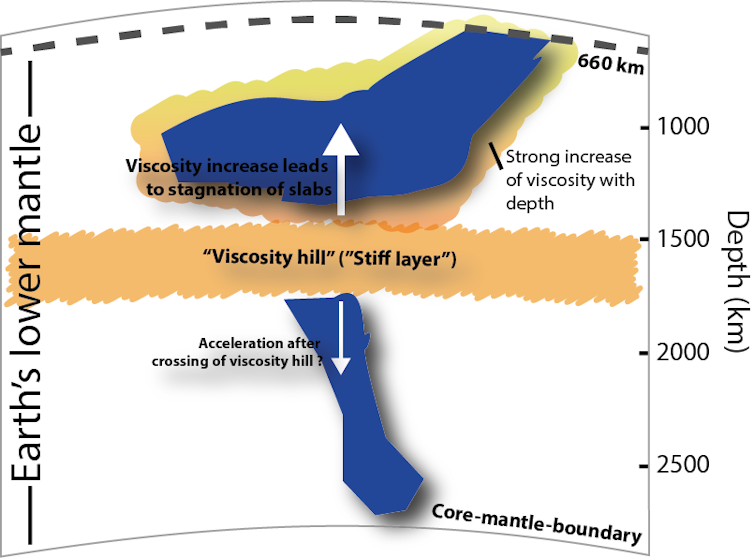 Source: theconversation.com
Source: theconversation.com
The rising of regions of the earths crust to higher elevations. New rock layers are always deposited on top of existing rock layers. Irregularly spaced blocks sink much faster than the regularly spaced array. Two dimensional numerical models are used to study the gravity driven sinking of a dense boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. Therefore deeper layers must be older than layers closer to the surface.
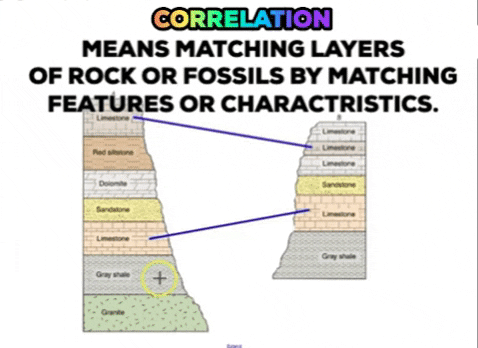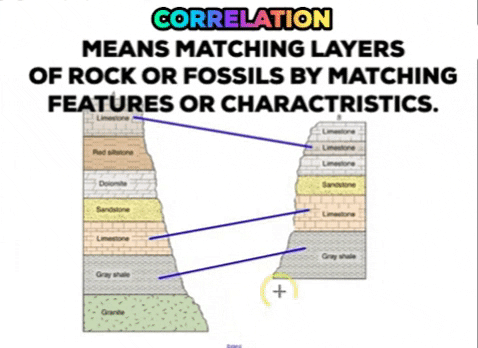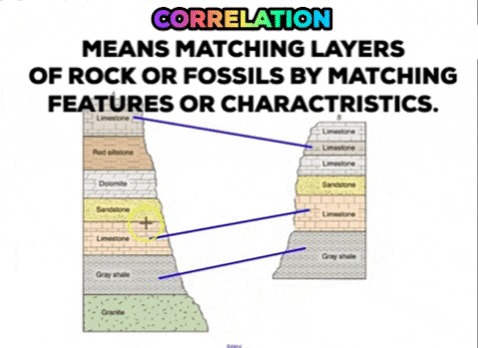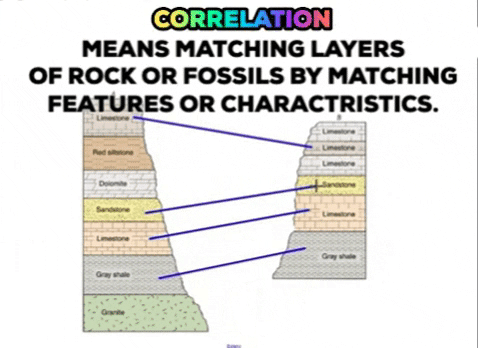 Source: uag-earthsci.blogspot.com
Source: uag-earthsci.blogspot.com
The rising of regions of the earths crust to higher elevations. The definition of subsidence is not restricted by the rate magnitude or area involved in the downward movement. We study gravity driven sinking of a boudinaged anhydrite layer within rock salt. For these reasons it is important to consider the possible effects of sinking in the scour protection design and to understand the mechanisms that could lead to unacceptable sinking of the scour protection the study showed that the sinking is controlled by two mechanisms. Therefore deeper layers must be older than layers closer to the surface.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title sinking of rock layers by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.